In the pursuit of redefining urban landscapes, the introduction of floating parks and clubs has marked a significant shift in how cities utilize their waterways. This innovative concept not only expands recreational spaces but also promotes sustainability and community engagement in densely populated areas. Let’s explore how real-world examples have set the stage for this transformative movement.

Embracing the Waterfront
Cities worldwide are increasingly recognizing their underutilized waterways as assets rather than obstacles. Floating parks and clubs are emerging as vibrant, community-focused spaces that offer an escape from the urban sprawl without the need for extensive land use.

Case Study: Copenhagen’s Harbour Baths
Copenhagen has long been a pioneer in urban water use, and the Harbour Baths are a prime example of this innovative approach. Designed by renowned architects, these floating recreational areas have turned the city’s waterfront into a bustling social hub. The baths are not only a place for swimming but also serve as venues for events and community gatherings, effectively blending recreational and social functions.


Case Study: Badeschiff, Berlin
In Berlin, Badeschiff or “bathing ship” is another excellent example of floating recreational use. Initially conceived as an art project, it has become a permanent summer attraction. This floating pool on the River Spree offers residents and tourists alike a unique swimming experience with panoramic views of the city’s skyline. The adjacent floating beach, complete with sand and lounge chairs, transforms the space into an urban oasis.


Sustainable Design Principles
These projects emphasize sustainability through the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly construction practices. The floating structures are designed to have minimal impact on the aquatic environment, showcasing how modern engineering can align with ecological preservation.

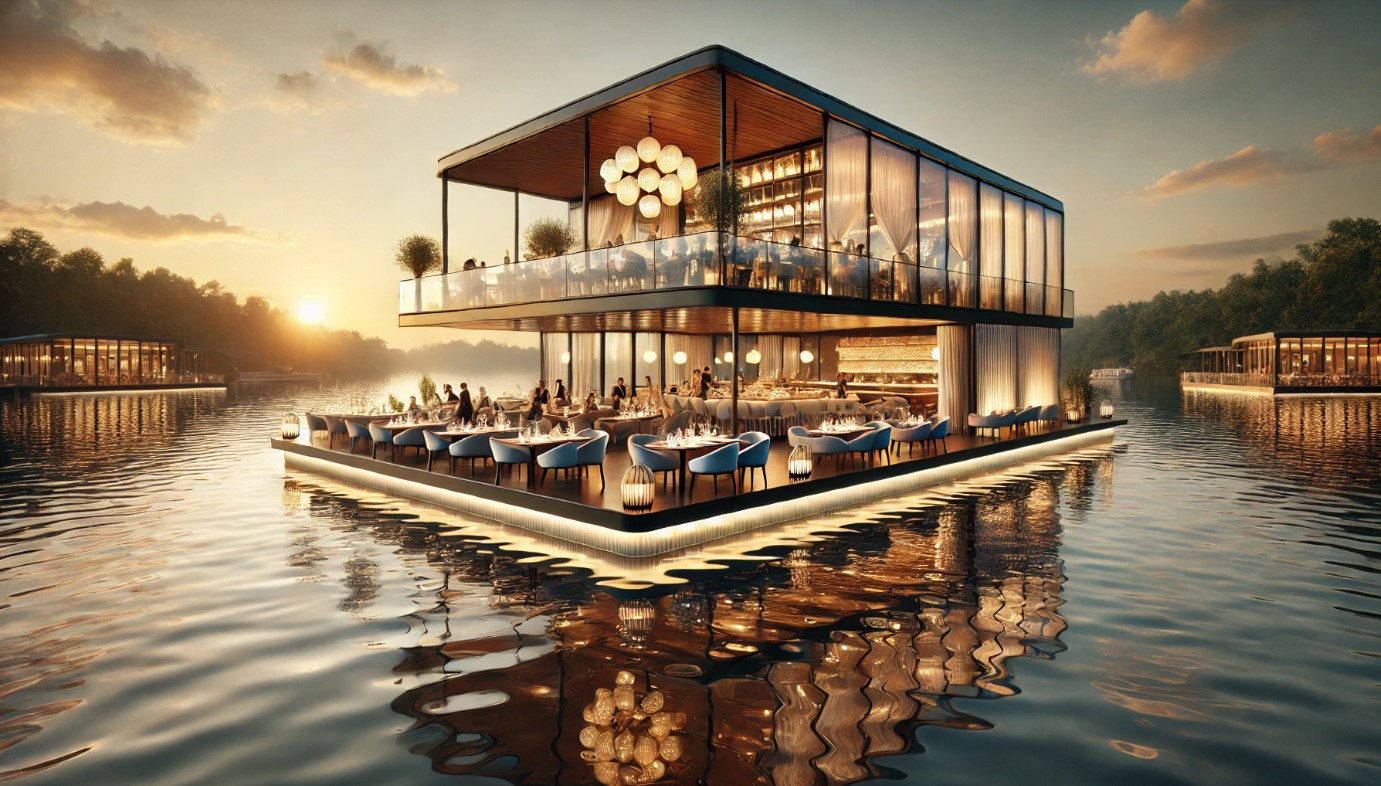
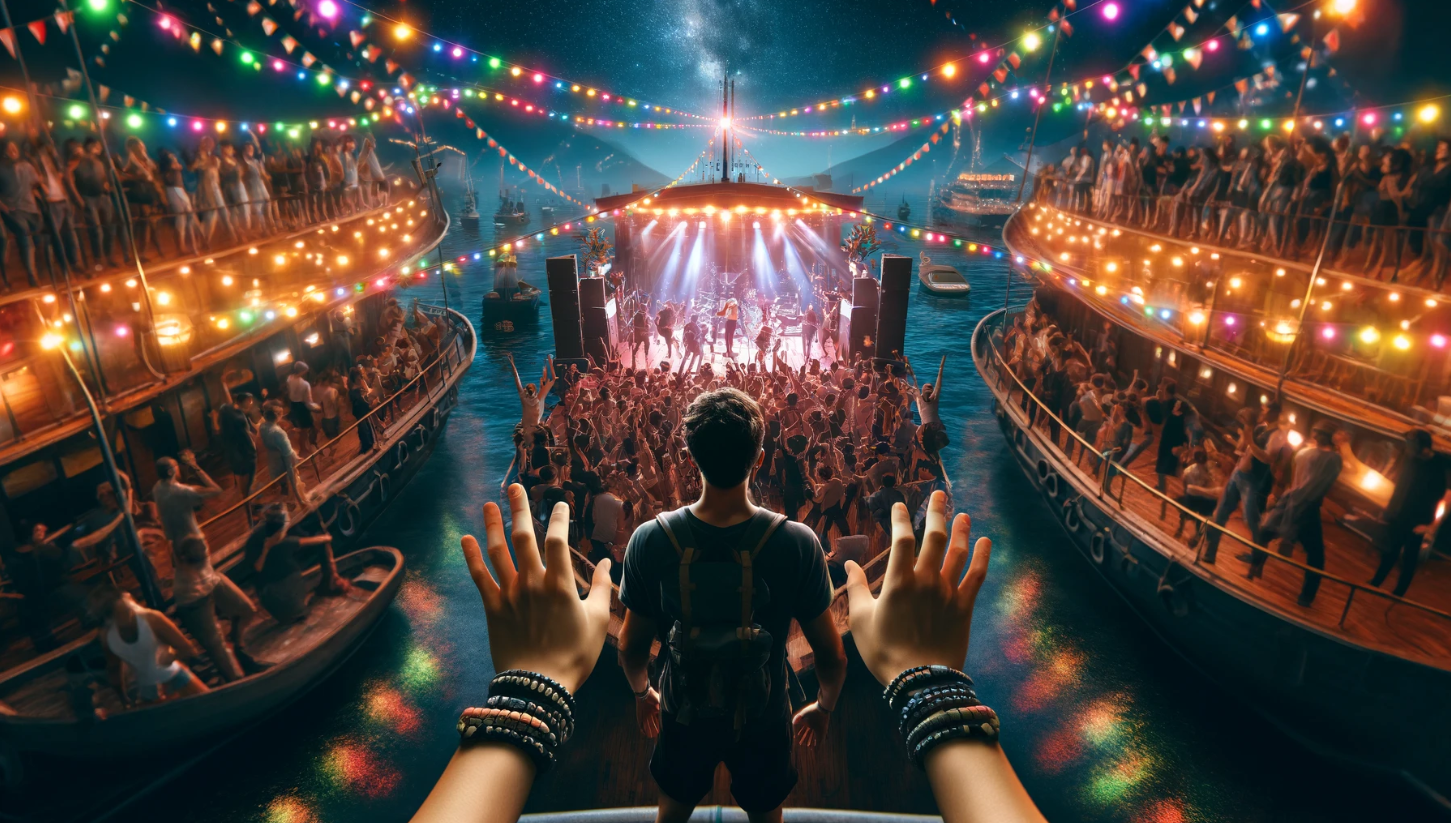
The Allure of Floating Clubs
Floating clubs extend the concept of water-based recreation into the nightlife scene. These venues provide unique experiences that combine dining, entertainment, and spectacular water views, redefining what a night out can look like.

Community and Connectivity
Floating parks and clubs are more than just novel attractions; they are part of a broader strategy to enhance urban life. They provide accessible, health-promoting recreational spaces in areas where land is scarce, fostering a sense of community among city dwellers.

Conclusion
The implementation of floating parks and clubs around the world serves as a testament to the possibilities of innovative urban planning. These spaces not only enhance the aesthetic and functional aspects of the cities but also promote a lifestyle that values sustainability, community, and well-being. As urban areas continue to grow, the integration of such water-based recreational facilities will play a crucial role in shaping liveable, resilient cities.